HowTo: Integrate Remote Desktop Services into MyWorkspace
Summary
Matrix42 MyWorkspace allows to integrate the Microsoft Remote Desktop Services seamlessly. The major goal of this integration is that every end user gets access to native hosted Windows applications side-by-side to modern Software as a Service and Web applications. This includes direct clientless access within every HTML5 browser without any restrictions to the underlaying device. The following visual describes the high level architecture of a seamless MyWorkspace Remote Desktop Services (RDS) integration:
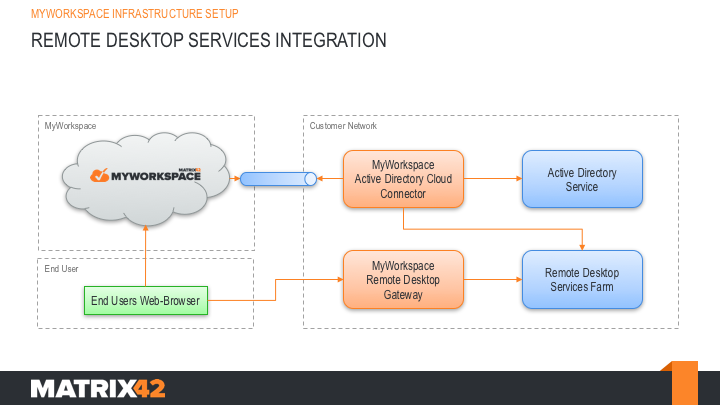
There are two main components which are involved into the RDS integration, the MyWorkspace AD Connector and the MyWorkspace Remote Desktop Gateway. Both togethe will inject remote applications directly into the launchpad of the end user dependent on the defined access rights.
Goal
After completing this how-to you will be able to integrate Remote Desktop Service farms hosted on-premise and in the cloud. This allows enterprises to offer end users access to legacy hosted Windows applications from any where any device without any client prerequisites.
First Step: Connect your Active Directory with MyWorkspace
MyWorkspace needs to be able to query which user has which permission in the Remote Desktop Services farm. Please follow the existing video tutorial how to connect an existing Active Directory with MyWorkspace: Video.
This step is repeatable for every Active Directory Domain (Forrest) which needs to be integrated into MyWorkspace. If you are unsure which AD needs to be integrated, use the domain your RDS servers are part of.
Second Step: Bind Remote Desktop Services with MyWorkspace
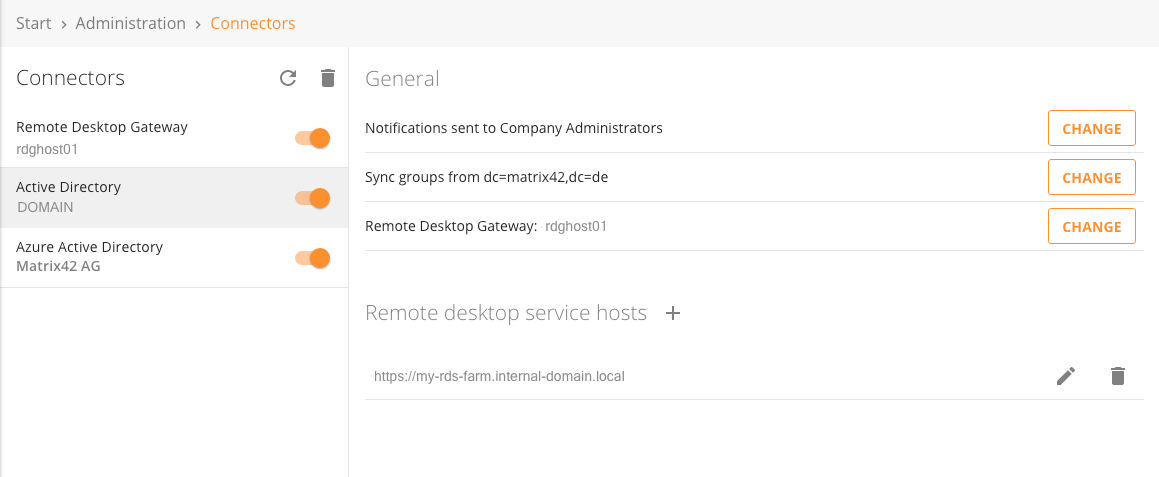
As soon the AD connector is correctly in place it's required to bind the existing Remote Desktop Services farm with the AD connector. Visit the connectors page, select the required AD connector and provide host Urls for the web interface of the Remote Desktop Service. This Urls does not to be available from the internet, only the host where the AD connector is installed needs to be able to get a connection to this service.
Third Step: Deploy a Remote Desktop Gateway
The HTML5 RDP client is part of the MyWorkspace Remote Desktop gateway which is available as a public cloud service or can be installed as an on-promise appliance next to the Remote Desktop Services. In general the remote desktop gateway should be installed on-premise into the customers data center to ensure that no RDP ports needs to be exposed to the internet. This increases the security of the whole infrastructure.
The following tutorial explains step-by-step how a remote desktop gateway can be installed: Getting Started with the Matrix42 Remote Desktop
Fourth Step: Connect the Remote Desktop Gateway with the Active Directory Connector
Last but not least re-visit the connectors page and select the previously installed remote desktop gateway as the responsible gateway for the active directory connector which is managing the Remote Desktop Services farm.
As soon this last step is executed the user will see all remote apps published in the Remote Desktop Services farm within the MyWorkspace Launchpad. Also all other third party clients like the MyWorkspace Browser Extension will show remote apps as usable applications as well. As soon an application is selected the system will launch this application through the HTML5 RDP client embedded is the remote desktop gateway. It doesn't matter which identity provider was initially used as long the e-mail address maintained in the active directory is the same as the mail address (nameID) received from the identity provider.