Managing organizational units
Overview
Organizational units represent the organizational structure of your company. This structure can be a hierarchy and typically includes the following elements:
- Independent organizational units (for example, subsidiaries)
- Business and functional divisions
- Departments
- Groups and teams
In a hierarchical structure, organizational units represent your business functionality, divisions, departments, etc. The Global organizational unit is generated during the installation, is the uppermost element in the organizational hierarchy, and must not be deleted. Configuration items that are not explicitly assigned to another organizational unit, belong to the Global organizational unit. You can add organizational units manually or import them in bulk using the standard template.
Assignment of contracts or employees, for example, to organizational units can later be used to give the users different permissions for managing the stored data. User permissions are defined by the roles that are assigned to them individually, so the permissions are granted to or withdrawn from a role.
Organizational units are managed in the Master Data application under Organization Structure > Organizational Units.
The validity period (from/until) is not monitored by the system and no status update is done automatically.
For any organizational unit except the Global one you can run the Set Compliance Company Code action. Having a compliance company code indicates that license compliance for this organizational unit is managed separately from other units.
How to import organizational units
Running the Import action
Execute the Import Organizational Units:
-
The Quick Import wizard will open.
- On the first page keep the Use existing import definition checkbox selected.
- Then click the Download Template File link.
- Open the file and fill in the data to be imported into the system.
- Upload this file.
- Follow through with the other steps of the wizard.
- After you click the Import button, the system will process the data. Upon completion you will see the import result message and a link to an import log file.
The Quick Import concept indicates that records can be imported from the corresponding navigation item by running the Import action. To be able to import records for any configuration item, an import definition for this configuration item must exist. An import definition sets the rules for importing data.
Common rules to consider when editing the import template file:
- Culture context of the data: when entering the text, consider the language specified in the quick import settings. It is important especially if the Excel file is uploaded as it may contain country-specific data such as dates, number formats, or currencies.
- Ambiguous values for matching attributes: if no or more than one matching values are found during processing of data, the value that is specified in the data source file is not saved to the system database.
Explanation of the import template
All imported data can be modified manually in the user interface.
| Field Name | Explanation | Maximum Character Length |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation | Required: key data used as the identifier for the import. Alphanumeric string. | 50 |
| Name | Required: alphanumeric string. | 100 |
| Type |
Specify one of the default options:
|
|
| Description | Alphanumeric string. | 1000 |
| Status | Two options are possible: Active and Inactive. When entering the text, consider the language that was set for the user interface. | |
| Valid from | Date. | |
| Valid until | Date. | |
| Org.Unit | Abbreviation of the parent organizational unit. | |
| Manager | Manager or responsible user assigned to the organization unit. According to the pre-configured mapping rules, use the following data template:
|
Example of importing organizational units
The given example is a filled-out template to be imported:

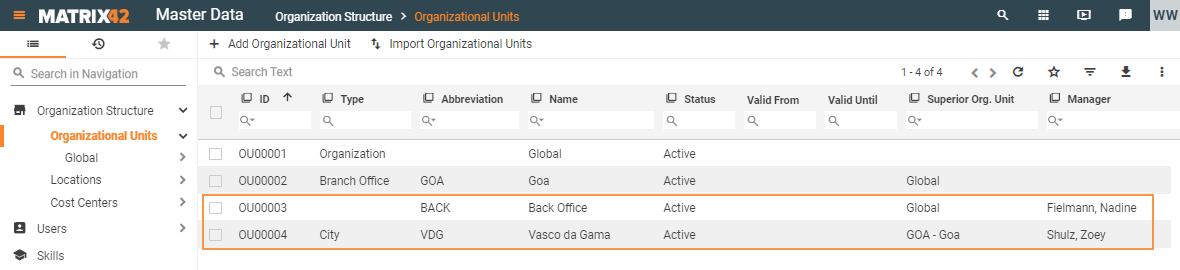
The successfully completed import results in the following records in the Organization Structure > Organizational Units navigation item:
Configuring Login Theme for the Organizational Unit
Starting with Enterprise Service Management Platform 12.1.3, it is possible to tailor the login experience per organization. The login page is configured in Themes and assigned to the customer or department in the Master Data application → Organizational Structure → Organizational Units edit page → General → Login Theme field, as shown in the following example:

Personalized Login Page configuration per Organizational Units is available for ITSM 2023 Advanced / Enterprise / ITSM 2025 Enteprise and works in the New Look design only.
See also Login Page Configuration.