Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
This chapter will help you overcome the most common problems with Matrix42 Full Disk Encryption.
Check that version is up-to-date. As a first step in troubleshooting, make sure that your Full Disk Encryption version is up to date.
Matrix42 has some requirements and unsupported software or hardware configurations.
The following configurations are not supported:
- Dynamic disks
- Computers encrypted with other 3rd party encryption solutions
- Microsoft Device encryption
- Non-NTFS drives like: FAT, exFAT
- BIOS MBR with 4 primary partitions
- RAID configurations (not supported on BIOS systems; on UEFI systems it is supported, but PBA works only in the Simple PBA mode)
In most cases Matrix42 FDE installation package can detect incompatible configurations during the installation or initialization and return the error messages explaining why the installation was not possible. Sometimes additional tools are required to understand why the installation or initialization fails.
New installation cannot be performed if the previous version of Matrix42 was uninstalled and reboot is pending.
Additional tools to get configuration details
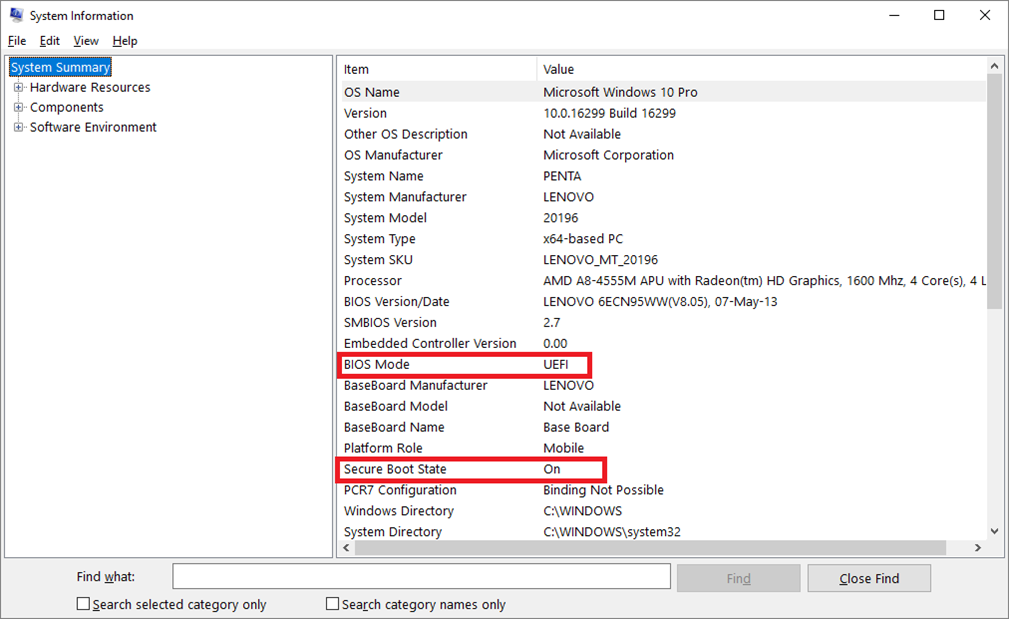
System Information
To start, press Windows + R and start msinfo32.exe. The tool can show the current status of Secure Boot, BIOS type.
Disk Management
To start, right-click the Windows icon and select Disk Management.
- Only Basic disks are supported in Matrix42 FDE. Dynamic Disks are not supported. You can check the disk type in the Disk Management tool.
- Disk Management can show the file system, only NTFS is supported.
- It also shows the status of BitLocker in the File System Column for the drives if BitLocker is Enabled.
- BIOS MBR with 4 primary partitions can also be seen in this tool.
- The presence of EFI partition usually is a sign of UEFI system.

The limit of 4 primary partitions is reached
Problem. BIOS MBR scheme has a limit of 4 primary partitions. Matrix42 PBA requires additional primary partition, which is created after the Matrix42 installation and during the FDE initialization. If there are 4 primary partitions in the system, the Matrix42 PBA partition cannot be created.
Solution. In most cases it is possible to delete one of the primary partitions to let Matrix42 FDE create required partition. For example, some HP laptops with MBR have 4 partitions used. One of the partitions is HP Tools. You can copy HP tools content to some local folder or removable media and erase the partition.
New systems with UEFI and GPT don’t have a limitation of 4 primary partitions.
BSOD happens on a first reboot after the installation
Problem. The Matrix42 FDE was installed, but the blue screen happened during the next reboot.
Solution. Disable filter drivers via Windows PE recovery tool.
- Boot the system using Windows PE removable media (you can use Matrix42 Recovery USB or CD which is also based on Windows PE).
- call: REG LOAD HKLM\fdesys c:\windows\system32\config\system
- call: regedit.exe
- delete "nbfdenc" filter name only from HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\fdesys\ControlSet001\Control\Class\{71A27CDD-812A-11D0-BEC7-08002BE2092F}\LowerFilters
- Leave other filters!
- delete "nbfdenc" filter name only from HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\fdesys\ControlSet001\Control\Class\{4D36E967-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}\UpperFilters
- Leave other filters!
- close regedit
- call: REG UNLOAD HKLM\fdesys
- Restart Windows.
System fails to boot Windows after disk encryption
If the systems fail to boot from the encrypted drive, there is an option to decrypt drive using Matrix42 Recovery Media. It might be a bootable USB stick or CD/DVD. For details, see the Matrix42 FDE - Administration and Usage Guide, chapter 1.12.
Always save ERI (Emergency Recovery Information) files and keep them in a safe place. This allows to decrypt encrypted drives. Once it is done, you can continue troubleshooting using other methods described in this document.
If there is no ERI file, ERI cache is not available, Helpdesk is not available or you do not remember the encryption key length and algorithm you cannot recover your data. Your data is lost. In case of an encrypted drive the data can be recovered only if the ERI file has been saved to an external and secure location (to removable media). Remove the NTFS compression to gain access to encrypted files.
Problems with image creation
Problem. An image of the complete hard disk has been made (to include the Windows and PBA partitions) using an imaging application such as Norton Ghost or Acronis TrueImage. When the image is transferred back to the same computer or to another computer of the same model, the computer does not boot.
Cause. Imaging applications use varying methods of data backup, compression, and optimization – using such methods may change the internal data structure of the encrypted partition and/or PBA partition.
Solution. There are two methods of imaging that are dependent on whether you want to encrypt the complete hard disk or just the system partition:
- If you want to make an image of the Windows partition AND our Linux (PBA) partition, you have to create an image using a sector-for-sector, uncompressed method.
- If you want to make an image of only the system partition and leave the Linux (PBA) partition as it is, then you have to create an image using a sector-for-sector method, but you have the option to use compression to make the image smaller. For more details, refer to Matrix42 FDE - Administration and Usage Guide.
Problems when copying an image back to the hard disk
Problem. The hard disk image (that you wish to re-apply) was created at a time when Matrix42 Full Disk Encryption was not installed on the computer (i.e. Matrix42 Full Disk Encryptions not in the image file). At the time you want to copy the image back to the target computer, Matrix42 Full Disk Encryptions installed and the PBA is initialized. After the image has been applied the computer will not boot from the PBA into Windows.
Cause. The PBA can no longer locate the necessary boot files.
Try one of the following:
- Use either the Matrix42 ERD to remove the PBA and reinstall Matrix42 Full Disk Encryption once you can boot to Windows, or…
- Perform a secure erase on the complete hard disk and re-copy the image back to the drive.
Applies to standard hard disks only (FDE with PBA).
Problem. The data contained in the hard disk image was encrypted by Matrix42 at the time the image was created (i.e. the image contains encrypted data). Matrix42 Full Disk Encryptions installed and the PBA is initialized on the target computer. The intention is to simply copy the data back to the hard disk and use the existing PBA. After the image has been applied the computer will not boot from the PBA into Windows. Cause.
- The PBA can no longer locate the necessary boot files.
- The Matrix42 Full Disk Encryption versions (between the image file and the current PBA) are incompatible.
Solution. Try one of the following:
- Use either the Matrix42 ERD (plus a valid ERI file) to remove the PBA and, if necessary, decrypt the drive, or…
- Perform a deletion/secure erase on the complete hard disk and re-copy the image back to the drive. Afterwards, decrypt the drive using the ERD (plus ERI file that is valid for the data contained in the image).
Characters cannot be entered into the HelpDesk dialogs
Problem.
- I am having trouble with the characters I pass on to the HelpDesk administrator. The computer keeps beeping.
- I am having trouble with the characters the HelpDesk administrator gives me. The computer keeps beeping.
Cause. Certain letters have been removed from the challenge/response process because they can be confused with another letter or number.
Solution. The following letters cannot be entered into the challenge/response fields in the HelpDesk GUIs:
B, D, O, Y
Every time you press a key for one of these letters the computer will beep to let you know that the entry is incorrect. The correct characters for each of the letters removed are:
| Problem Letter | Correct characters |
|---|---|
|
B (for Bravo) |
8 (eight) |
|
D (for Delta) |
0 (zero) |
|
O (for Oscar) |
0 (zero) |
|
Y (for Yankee) |
V (for Victor) |
Prevent specific users from being “captured” during self initialization
Problem. When the computer boots into the PBA component an unknown user entry is visible in the PBA login dialog.
Solution. You can define users to be ‘blacklisted’ to prevent them being ‘captured’ upon PBA self initialization, for example netinstall or ‘__vmware_user__’. This is achieved by editing a Matrix42 registry entry that acts as a blacklist (the entry ‘__vmware_user__’ has already been added to the list).
Follow these steps to add a user to the blacklist:
- Open the Windows registry editor by either selecting Start>Run and entering regedit into the Open field, or double-clicking the regedit.exe directly in the directory: C:\WINDOWS\regedit.exe
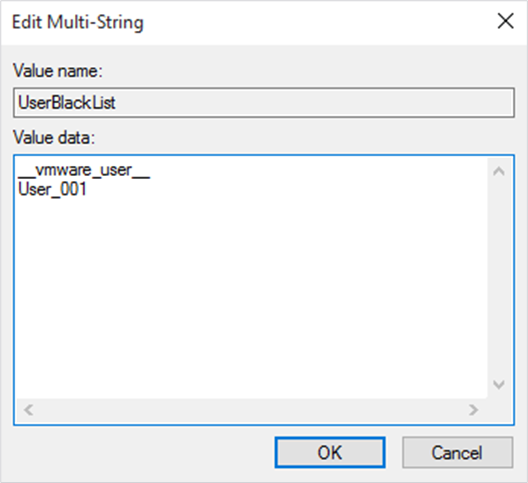
- In the registry editor open the entry: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\cpsd\SBS\scopen\UserBlackList
- The Edit Multi String dialog appears:

-
Place and click the cursor under the last, current entry in the Value data pane and enter the exact characters for the user to be blacklisted. If you want to create more than one entry, make sure that each entry starts on a new line. Click OK to apply the entries.
- Close the registry editor.
- Revert to original settings. If, at any time after you have made this change, you decide to revert to the default blacklist entries, then just delete all the registry entries except __vmware_user__ .
User capturing fails
The problem is [currently] specific to some Intel chipsets, for example chipsets used in DELL 630+830 computers.
Problem #1. ‘User capturing’ (i.e. Windows credentials) has been enabled and upon restart the following problems may occur:
- User capturing is apparently successful, but upon restarting the computer the self-initialization dialog reappears –i.e. user capturing was not successful.
- ither the PBA login screen does not appear or PBA itself does not appear.
Solution. This problem usually occurs because the Intel ICH 8 (AHCI) drivers are installed but the BIOS is configured for ATA mode.
If you download the ICH 8 driver from Intel, the package will not install unless the BIOS has configured the chipset for AHCI (you will be prompted that your system does not meet the minimum requirements). The driver on the DELL driver CD has no such restriction. The result is an installed ICH 8 driver that expects AHCI-mode but instead encounters an ATA-mode chipset.
It is recommended to remove Matrix42 Full Disk Encryption (if necessary using the Bart PE recovery CD) and reinstall Windows. The native Windows driver will allow you to install and perform user capturing without error.
Problem #2. “User capturing” (i.e. Windows credentials) has been enabled. When restarting the computer, the self-initialization dialog keeps reappearing – i.e. user capturing was not successful.
There is a conflict between the Intel ‘Network Provider Credentials Manager’ (IntelNetProvCredMan) and the Matrix42 capture driver. Follow these steps to change the provider order and enable successful user capturing:
- Click Start -> Control Panel -> Network Connections.
- From the menu, click Advanced -> Advanced Settings.
- The Advanced Settings dialog appears. Click the Provider Order tab.
- Make sure the entry Matrix42 is above the entry IntelNetProvCredMan. If not select the entry Matrix42, and click the ‘up’ arrow button until the entry appears above IntelNetProvCredMan.
- Click OK.
- Restart the computer to capture the Windows credentials. Start the computer again to confirm that you must enter the password in the PBA component.
Alternative solution. As an alternative you can use the following registry key to change the provider order:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\NetworkProvider\Order
Partition creation fails after FDE has been initialized
Problem. Data copied to a partition that was created after the Matrix42 FDE component has been initialized fails to appear in Windows.
Solution. The cause of this is most likely to be the sector-based encryption. A workaround is to perform a restart after creating the new partition. If the new partition contained sectors which were previously encrypted, then reformat the new partition after the restart.
Incorrect GUI language/Change GUI language
Problem. The control center GUI has the wrong language. The installer has incorrectly recognized the language of the operating system. This may happen if you are using a Windows MUI language pack on top of the original system language.
Solution. A registry entry needs to be changed.
- Open the Windows Registry Editor and navigate to: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\SECUDE\SNB.
- Create new string Value with the name lang (or double-click it if it already exists) and enter the correct language into the field Value Data.
- Matrix42 Full Disk Encryption currently supports the following languages:
- English (use en_US)
- German (use de_DE)
- Click OK when finished and close the editor.
- Restart the Matrix42 Full Disk Encryption Control Center.
Alternative way
Alternatively, you can:
- Open a simple text editor and copy/paste the following text to change the GUI to German (with spaces and gaps):
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\SECUDE\SNB]
"lang"="de_DE"
- Enter ‘en_US’ instead of ‘de_DE’ to change the GUI language to English
- Save the file and close the text editor.
- Change the extension of the file just created from *.txt to *.reg.
- Double-click the file to set the registry correctly.
Administrator password forgotten
Problem. Administrator password for Full Disk Encryption has been forgotten.
Solution. Decrypting partition with the help of the ERI file -> deleting FDE partition -> initializing FDE again.
For details about ERI file, see Matrix42 FDE - Administration and Usage Guide, chapter 1.12.
- If FDE was installed locally, the path for the ERI file is defined during ERI-file creating.
- If FDE was installed using Matrix42 Data Protection Console, the ERI file can be exported from the Console (Computer management | FDE | Administrator).

How to change PBA boot method
Problem. To date, general support of new computers is a costly and time consuming process – the sheer number of new notebook models grows every day. Each model brings new hardware and software with it – a challenge for any software that works so closely with the hardware.
That’s why after the PBA initialization, some problems with Windows starting may occur.
Solution.
Matrix42 utilizes the Grub boot loader in BIOS systems and the UEFI boot manager in UEFI systems. See solutions for:
BIOS
Call the grub menu to select the boot method, which will start your system correctly. To call the grub menu, press Ctrl + G key combination or only G key before the PBA boot image appears.
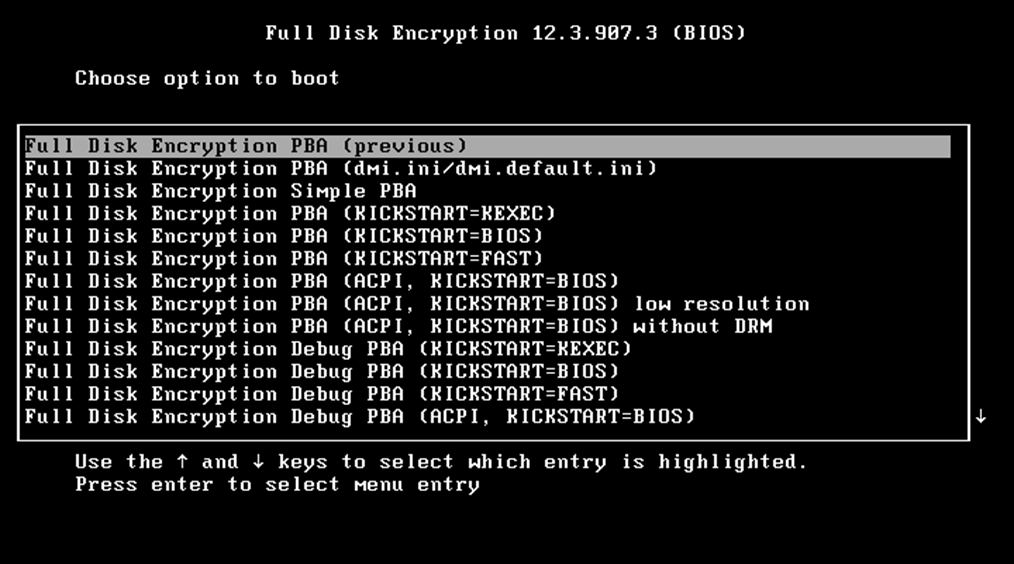
In this menu, select one of the following boot methods, and then press Enter.
UEFI
When the UEFI FDE entry appears on the screen, press the Ctrl + G combination or only G key. In the boot menu, select one of the methods.

Boot mechanism description
| Boot method | Details | |
| BIOS | UEFO | |
|
[any of the methods] |
The boot method that was selected the previous time. Full Disk Encryption PBA is a default value. | |
|
Full Disk Encryption PBA (dmi. ini/dmi. default. ini) |
The system is booted with the settings, which has been defined in the dmi.ini file. | - |
|
Full Disk Encryption Simple PBA (text-based mode) – in both BIOS and UEFI |
Simple PBA is an alternative PBA with a minimal feature set used to avoid possible hardware incompatibilities. During PBA, hardened Linux is used and during Simple PBA (SPBA), the Matrix42 Credentials manager is used. For details about PBA and SPBA in UEFI and BIOS systems, see Figure 52 and Figure 53. How it works? User authenticates with user name and password in a GUI-less login mask (in case of text-based mode) or in a GUI dialog (in case of graphical mode). HelpDesk works in all SPBA modes and smart card authentication works only in the graphical mode. What sources are used? Simple PBA utilizes the Grub boot loader in BIOS systems and the UEFI boot manager in UEFI systems. For details about PBA and SPBA comparison, see Figure 52 and Figure 53. |
|
|
Full Disk Encryption Simple PBA (graphical mode) – only for UEFI |
||
|
Full Disk Encryption PBA (KICKSTART=BIOS) |
This is a standard mechanism used by Matrix42 Full Disk Encryption and should not be edited. This involves rebooting the computer a second time so that the BIOS hardware settings can be passed to Windows | |
|
Full Disk Encryption PBA (KICKSTART=KEXEC) |
This mechanism is similar to KICKSTART=BIOS but does not need a reboot. | - |
|
Full Disk Encryption PBA (KICKSTART=FAST) |
This mechanism has been implemented for systems that have unusual hardware configurations not supported by the KEXEC mechanism. | |
|
Full Disk Encryption PBA (ACPI, KICKSTART=BIOS) |
This will automatically select an alternative Linux kernel configuration that enables ACPI support. This is something found almost exclusively in desktop computers and is rarely needed.ACPI mode is not compatible with Friendly Network. | - |
|
Low resolution |
Select this mode if during a previous boot, text and images of FDE dialogs were unreadable on the monitor (e.g.: on laptops). All boots after that will be performed in the selected mode with low screen resolution. For details about changing a screen resolution in PBA settings, see screen resolution. | |
|
Without DRM |
Select a mode without DRM if there are problems with graphic card and PBA loading. | |
|
Debug PBA |
Select a mode with this option to identify boot errors. Kernel loading messages will be displayed in this case. | |
|
HDD 1 Partition 1 |
A bootloader on the partition 1 of the hard drive 1 will be used to start the system. | - |
|
HDD 1 Partition 2 |
A bootloader on the partition 2 of the hard drive 1 will be used to start the system. | - |
|
HDD 1 Partition 3 |
A bootloader on the partition 3 of the hard drive 1 will be used to start the system. | - |
|
Windows Boot Manager |
- | This mechanism uses default Windows Boot Manager, without PBA. |
|
Change keyboard layout |
- | Select the keyboard layout for entering PBA credentials: German or English. |
Using KEXEC and FAST. The KEXEC and FAST mechanisms should be used only if the standard mechanism (BIOS) does not work.
Figure 52: PBA and SPBA comparison UEFI

Figure 53: PBA and SPBA comparison - BIOS

PBA fails to start in RAID mode
Problem. Matrix42 FDE installation completes successfully. Partition is created. Once PBA is activated, the system hangs on startup. Caps lock is flashing and nothing happens. There is no chance to press Ctrl + G key combination (or only G key) to change PBA boot method, because the system hangs before this phase.
Solution. Changing System Drive from RAID to AHCI.
Applies to Matrix42 Full Disk Encryption 11.2 and higher.
Enabling safe mode to avoid Windows crash. Before changing SSD type in BIOS, switch to safe mode. If not, Windows fails to boot and crashes. See the details below.
Prepare local administrative account. Please, make sure that local administrative account exists on the laptop and you know the password for this account. Network is disabled in this Safe Minimal mode and it might be not possible to authenticate and log in to the system.
Preparing Windows to start in safe mode
- Run msconfig.exe. The System configuration dialog appears.

- In the Boot tab, check Safe boot and set Minimal radio button.

- Click Apply and reboot the system.
- Press the key to Enter BIOS system setup (Esc, F1, F2, F10 or F12, depends on the device model). Change Storage Configuration option in BIOS from RAID to AHCI. Save settings and proceed with booting Windows.
- Once Windows is started successfully, run msconfig.exe and clear the Safe boot check box.
FDE initialization fails – very fragmented disk
Problem. FDE initialization fails, because a disk is very fragmented.
1st solution.
- Defragment the drive, using the Optimize option (for details, see the Microsoft article Defragment your Windows 10 PC).
- Shrink the volume manually (minimum size is 510 MB).
- Initialize FDE.
2nd solution (if 1st solution haven’t helped).
- Clear the Automatically manage paging file size for all drives check box.
- Go to Control Panel | System and Security | System.
- Click Advanced system settings.
- The System Properties dialog appears.
- In the Advanced tab, click Settings in the Performance area.
- The Performance Options dialog appears.
- Navigate to the Advanced tab and click Change button.
- The Virtual Memory dialog appears.

- Clear the Automatically manage paging file size for all drives option.
- Select the drive and then select the No paging file radio button.
- Click OK to save the changes and close the dialog.
- Restart a computer.
- Defragment the drive, using the Optimize option (for details, see the Microsoft article Defragment your Windows 10 PC).
- Shrink the volume manually (minimum size is 510 MB)
- Restore the settings the Virtual Memory settings to previous ones: enable the Automatically manage paging file size for all drives option and the previously selected radio button.
- Initialize FDE.
PBA error
Problem. The PRA ERROR message is displayed on the whole screen when loading an operating system.
The reason is that the PBA protection has triggered in response to the issues with the FDE loader.
Solution.
- Start the emergency recovery application (for details, see chapter “Emergency recovery via boot CD or USB stick” of the Matrix42 FDE - Administration and Usage Guide).
- Click Disable PBA load check under BootChain.
- The dialog appears.
- Click Start.
- Close the emergency recovery application.
- Continue the system loading.
BitLocker hang after BSOD
Problem. In certain circumstances BitLocker encryption/decryption may hang. In our test environment BSOD happened when FDE was uninstalled during BitLocker decryption; after that BitLocker decryption hung.
Solution. Use BitLocker manage-bde commands in the commandline to pause encryption/decryption and then start the reverse process. After that you can repeat disk encryption or decryption that hung.
- Run cmd as administrator.
- Enter manage-bde -pause command. E.g: enter manage-bde –pause C: to pause encryption/decryption on disk C.
- Start the reverse process.
- If decryption was performed, start encryption using the command manage-bde –on . E.g.: enter manage-bde –on C: to start encryption on disk C.
- If encryption was performed, start decryption using the command manage-bde –off . E.g.: enter manage-bde –off C: to start decryption on disk C.