Search Filters
Overview of Search Filters in Classic Look
Search filters are the most flexible way to search through large amounts of data by creating and editing search conditions.
This page is intended to explain the basics of the Matrix42 platform search filters and how any user who wants faster access to specific information can benefit from it.
Any user of the Matrix42 platform, would it be end-users, application administrators or any other person who has access the application can create, run, save and reuse the search filters.
At the same time, search filters are not intended to substitute the other provided by default search options of the Matrix42 platform.
Search options can be conventionally classified as:
- simple search has a set of forms that a user fills in, such as global search, keyword search on particular pages or through columns with specific data where the page layout is based on the Dataset View;
- advanced search or the search filters.
The search filters are yet another search option, which additionally provides numerous opportunities for:
All users:
- configuring advanced search criteria;
- creating simple queries with provided in the application hints;
- immediately retrieving results;
- saving and reusing search filters;
- providing quick access to the filters right from the application's navigation;
Application Administrators:
- creating, managing and sharing search filter settings to other users;
- mastering data queries by creating complex conditions defined as ASQL expressions in the search filters.
Instant data filtering
The main purpose of the advanced search is data filtering and instant retrieval of the results. Filtering criteria may include a number of complex conditions manually defined by a user. Search filter query can be:
- run and tested immediately;
- saved and reused as a part of the application navigation (locally, for the current user) or shared with other users of the application (globally, by an Administrator).
Search Filters list
A Search Filter is an object that allows users to define search criteria for Dataset Views and then use these predefined criteria in corresponding Advanced Searches, where users can run any combination of previously created and editable Search Filters.
You can view available Search Filters at:
- Administration application→ User Interface → Search Filters page with available search filters for all applications. You can access this page provided you have the required permissions.
- Any application of the Matrix42 platform:
- a page with a Dataset View layout →
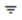 advanced search icon → Queries tab lists all available for the Dataset View queries;
advanced search icon → Queries tab lists all available for the Dataset View queries; - Navigation: users can also choose to display Search Filters in Navigation for easy access. Shown in Navigation search filters are marked with
 icon:
icon:
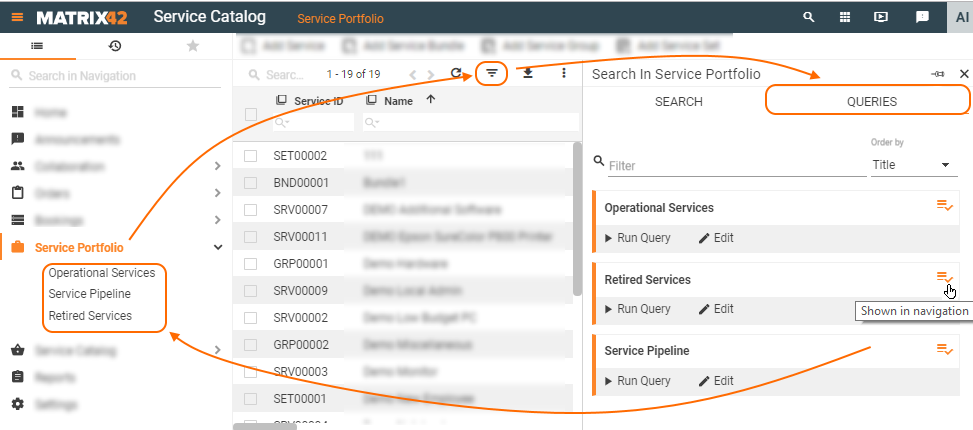
 Query filter icon lists all search filters that are available for the current Dataset View but are not displayed in the navigation and don't have a
Query filter icon lists all search filters that are available for the current Dataset View but are not displayed in the navigation and don't have a  icon in a list of all search queries:
icon in a list of all search queries:
- a page with a Dataset View layout →
Creating Search Filters
You can create and reuse Search Filters from:
- the User Interface of any application via:
- Customize Navigation option;
- Advanced Search;
- Administration application from the:
- User interface menu → Search Filters page;
- User interface menu → Layouts → Dataset Views settings → Filters tab.
User interface
To create a Search Filter for a specific page from the User Interface:
- Customize Navigation: right-click the Navigation Item → Customize Navigation Item → click Add Child Filter icon;
- Advanced Search: on any page that has
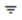 advanced search icon open Search tab → set a necessary condition and click Save:
advanced search icon open Search tab → set a necessary condition and click Save:
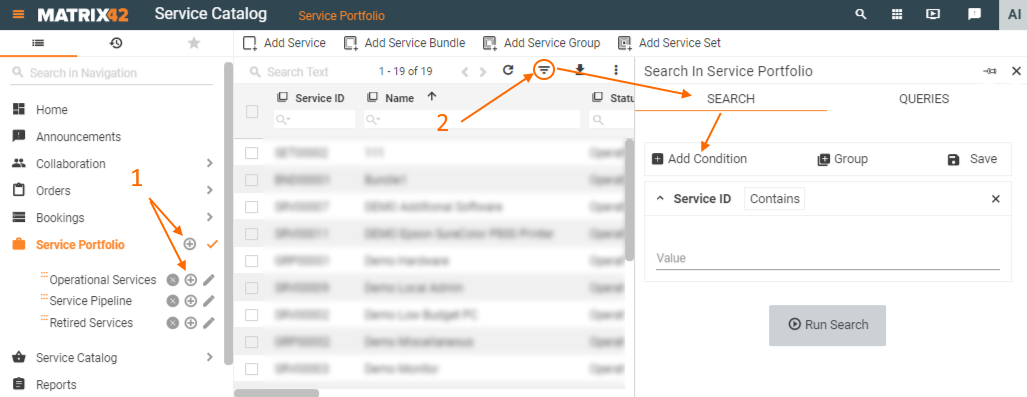
Fill out the following fields:
| Create a search filter example | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |
Title* |
name of the search filter. Required field. This title is displayed in the application's navigation if enabled. |
| Description | optional field that characterizes the search filters and describes their purpose. | |
| Position |
when the search filters are enabled in the application's navigation you may need to reorder their displaying position. Specify an integer to change the position of the search filters placed on the same nesting level of the navigation items hierarchy. Skip the field and the position will be assigned automatically. |
|
| Apply parent filters for all nested items |
This option is available just for root-parent queries.
|
|
| Show query in Navigation |
|
|
| Set as default filter for navigation item |
Search filter can also be assigned as default by an Administrator user while configuring a Navigation Item. |
|
| Specify Query conditions* | specify data filtering conditions in the provided query builder. |
Click Save or Done to apply changes.
Created search filters are not available for all users of the application by default.
- End-user: creates and applies search filter settings locally. No other user has access to them, except for the application Administrator.
- Administrator: creates search filters locally, for displaying only in his/her user account. Additionally, the Administrator can share access to any filters created by any user of the system globally, for the entire application, user roles, user groups, etc. When a filter owner deletes the search filter it is deleted for everyone who had shared access to this filter.
Advanced options
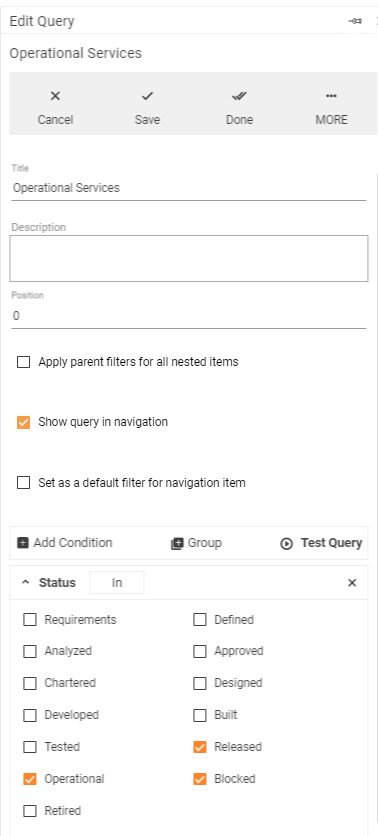
Administrator only can see the list of advanced search filter settings by clicking More button:
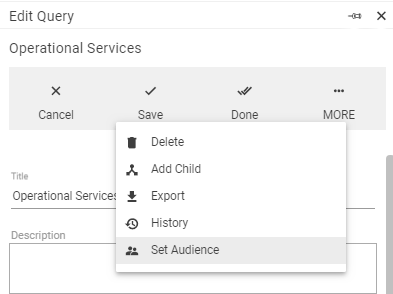
Administration
To create a Search Filter from the Search Filters grid go to Administration application→ User Interface → Search Filters → Add Data Query Filter and fill out the following fields:
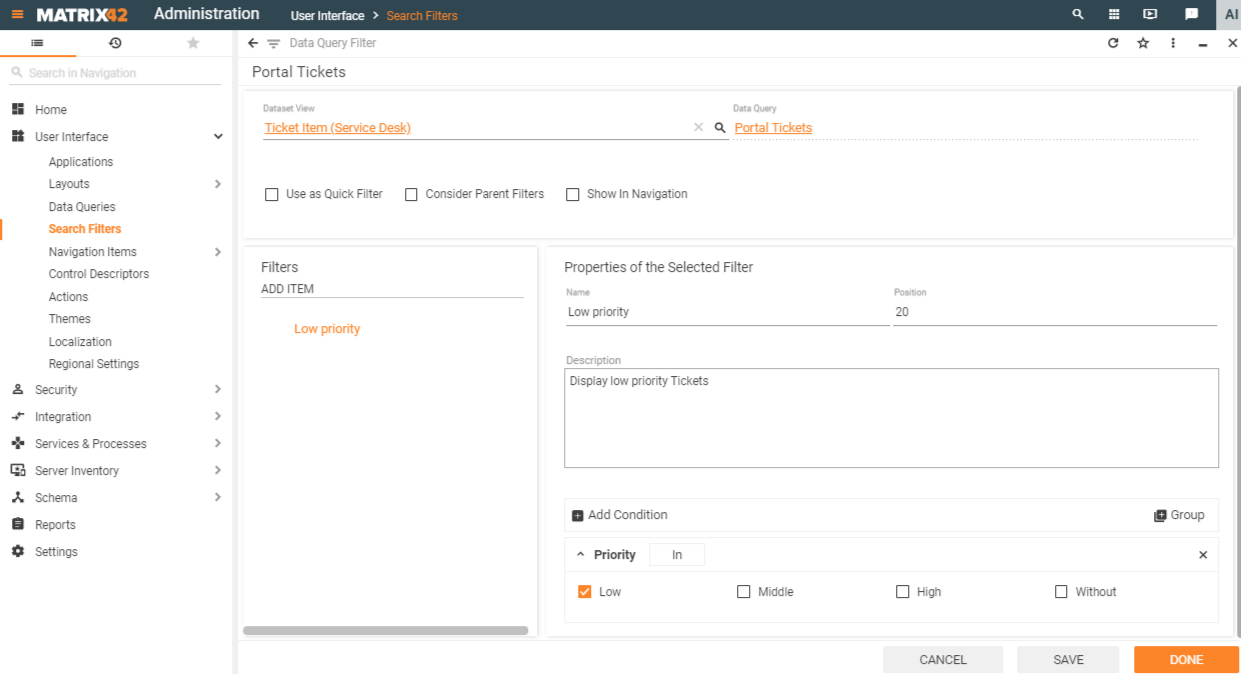
The set of fields and settings is mostly the same as in the User Interface.
Additional settings are:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Dataset View |
Choose a page layout of Dataset View type for which you would like to create a Search Filter. Start typing the name of the Dataset View for suggestions of the layout and application where it is used. The User Interface does not require this field as the Dataset View is automatically detected by the system based on the page you have opened. |
| Data Query |
Data Query is automatically detected and assigned based on the selected Dataset View. Data Query pre-defines a set of fields that can be queried by the search filter. |
| Use as Quick Filter |
checkbox options:
|
| Filters | click ADD ITEM and specify the Name, Description, Position, and query conditions for the Search Filter. |
Click DONE to save the changes and close the page.
At this stage, the search filter is not available anywhere except for the Administration application Search Filters list.
Set audience by default is set to restricted and therefore the search filter is not visible in the advanced search tab or in the Navigation even if its display is enabled.
Localization
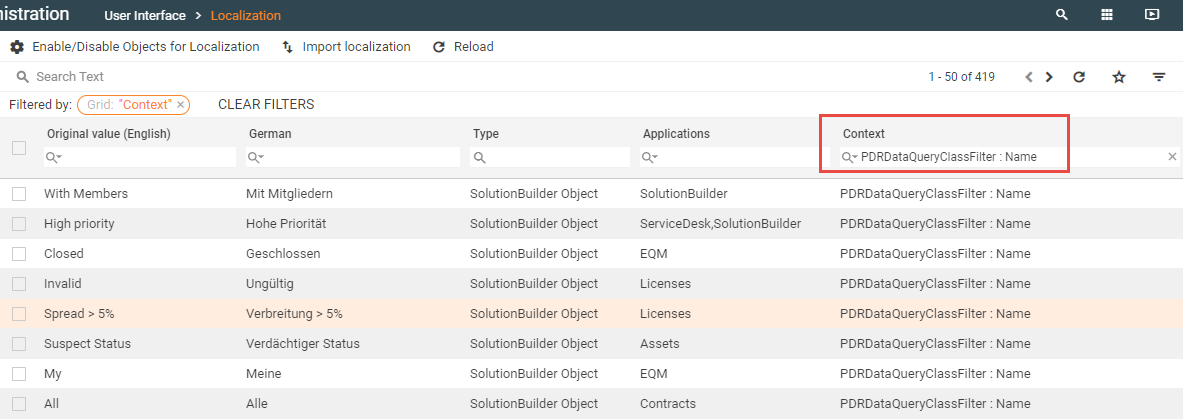
The Data Query Filter dialog does not support the localization of the Filters in the "Localization Mode". The localizing of the Filters can be fulfilled in the "Administration / User Interface / Localization" area. To show only the Data Query Filter in the grid, filter the Localization string Context to "PDRDataQueryClassFilter : Name"
Specifying search query conditions
Basic terms and principles
Search filters are based on queries or questions with one or multiple conditions expressed in a formal way. Search filters allow users to create complex questions and as a result, retrieve more specific information that meets their goals and facilitates their day-to-day work in the Matrix42 applications.
A query has the following parts:
- Field: a specific type of information which serves as a source of the data that will be searched through. In a technical sense, this information is an attribute or the column name of a database table, for example, user id, incident summary, service description etc. Displayed in the drop-down list fields are pre-defined by the corresponding to the current layout Data Query. Only columns with the Search Display Type option set to "Yes" are available.
- Value: the actual data or an equivalent of the search keyword you are looking for in the filtered data. Value may also be pre-defined according to the selected field type (e.g. true/false) or may require manual data input;
- Operator: a reserved word that is used to perform the comparison, arithmetical or logical operations and relate the selected field to a specified value. Common operators include equals, not equals, is set, contains, less than, etc. and are auto-suggested.
Query builder of the advanced search provides hints with all available for the selected field operators.
- Condition: query builder provides AND condition and OR condition which can be combined in Group and used to filter records based on more than one condition. When combining conditions Group acts just as parentheses in maths so that the database knows in what order to evaluate each condition.
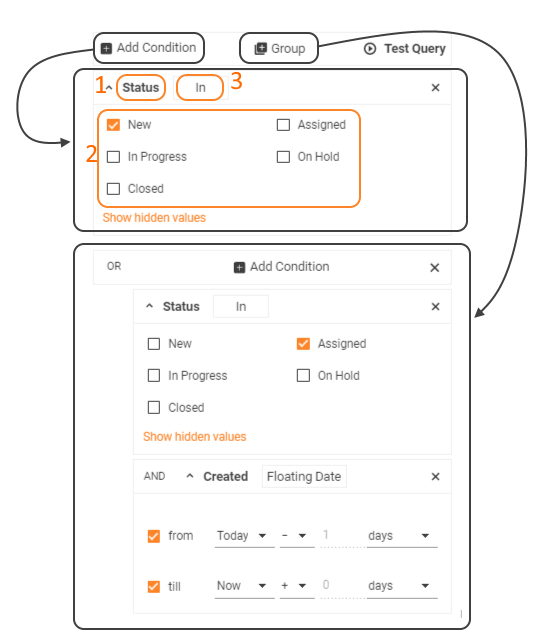
Editing search filter query conditions in the User Interface
Add as many conditions to the new Search Filter as you need and click Save.
You can add and set up as many Search Filters for the same Dataset View as you need.
Operators in Search Filters
Advanced options: Expressions
Advanced Users have the option to create a Search Filter based on the Expression condition, where they can provide any ASQL based query.
This option allows creating complex queries and is available for Administrators only.
So the Expression field takes an ASQL query as its value as follows:
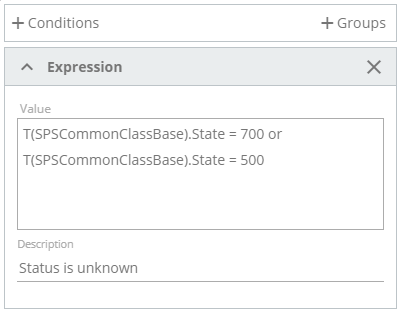
Description of an entered query is required as the value, in this case, may nor be self-descriptive as in the other set of fields provided for a Dataset Query.
Attribute-based operators
When a user selects one of the suggested fields, the available operators are automatically provided based on the type of the selected data attribute:
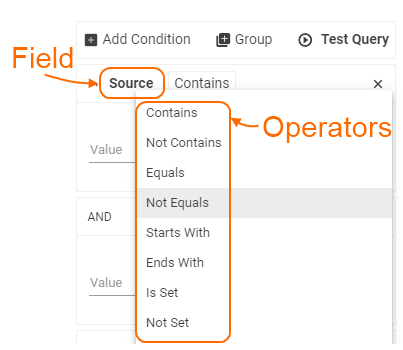
So depending on the field the user selects in condition picker, different operators are available:
| Field/ attribute type | Available operators |
|---|---|
| Date time |
|
| Pickup |
|
| Text |
|
| Relation | |
| Boolean |
|
Search Filters In Navigation
Displaying in Navigation
To add a Search Filter to Navigation enable Show in Navigation check-box of the Search filter settings.
Assigning default search filters
Use the Set as default filter for Navigation item property setting to change the application's navigation.
Using Search Filters
Instant advanced search
Specify conditions and Run the Search Filter from the Advanced Search panel to instantly retrieve the results, without having to save and configure the search filter additional properties:
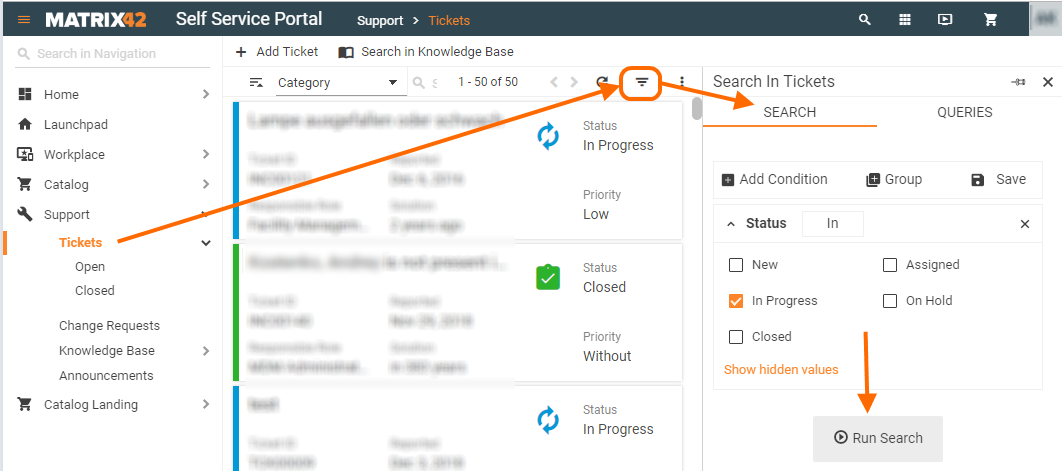
Advanced Search Queries
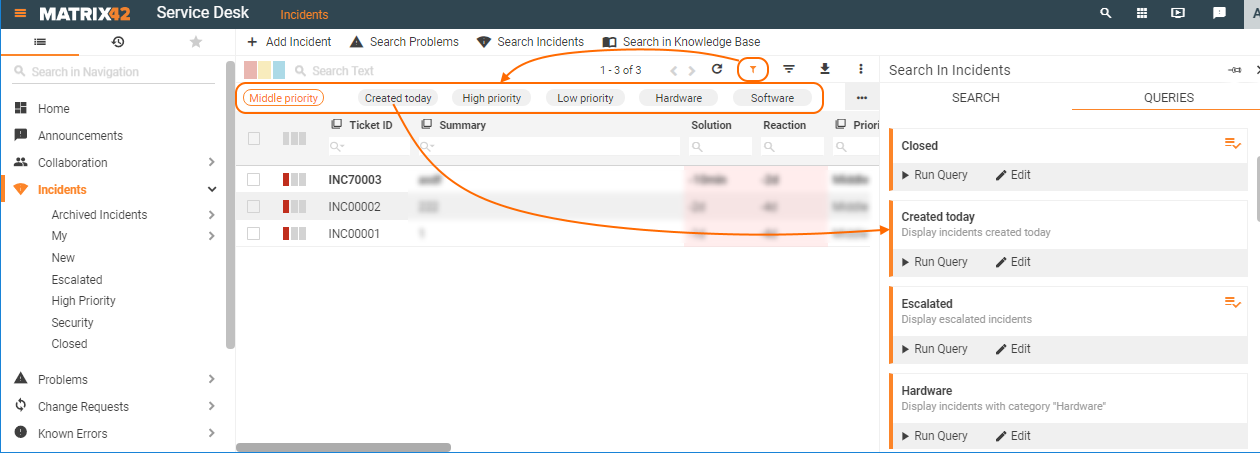
To use Search Filters in Advanced Search:
- Open the corresponding Dataset View;
- Click the Advanced Search icon;
- Queries tab lists all the previously created Search Filters.
- Click the Run Query button to instantly retrieve the results:
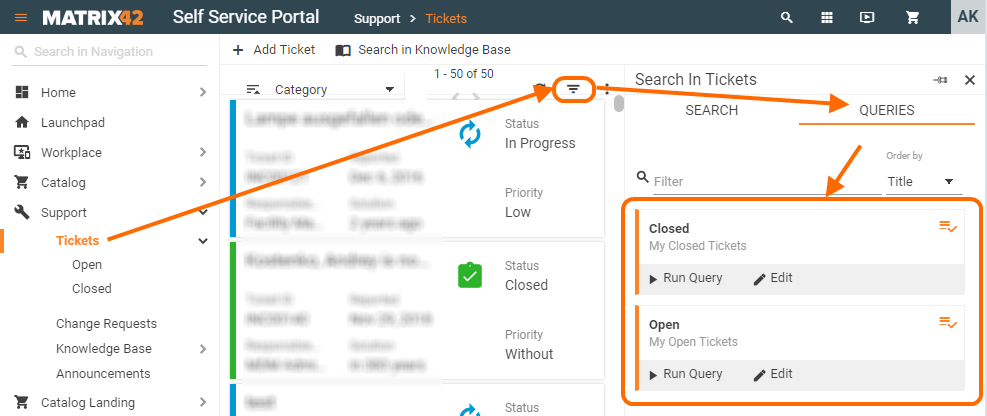
Query Filter
Search filters which are available for the current Dataset view but not shown in the application's navigation can be applied via  Query filter icon:
Query filter icon:
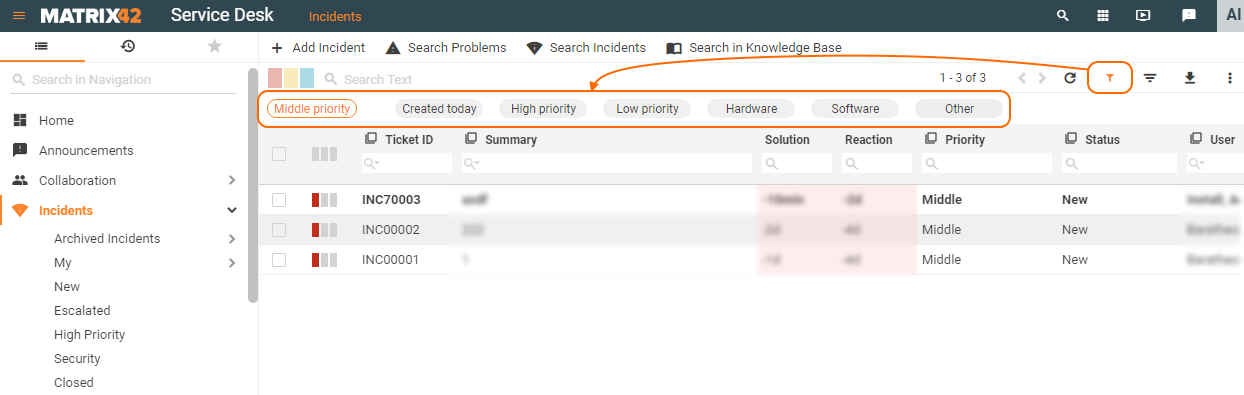
Navigation
Some of the search filters are displayed in the application's navigation. The filter is applied automatically when you click on it:
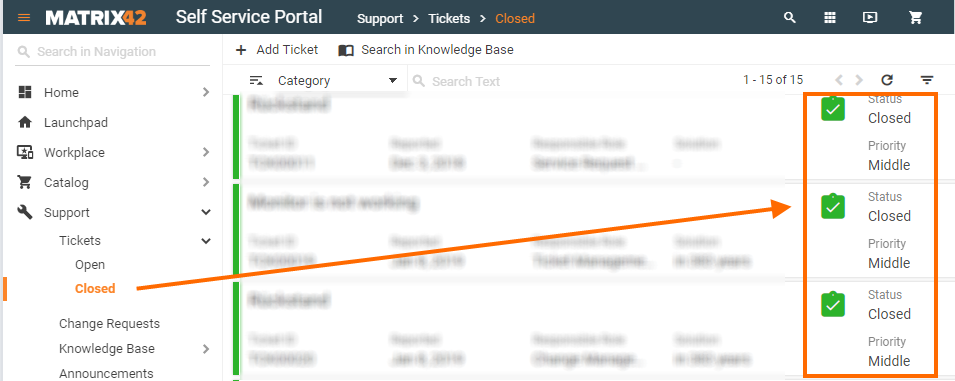
Overview Search Filters in New Look
Search filters are the most flexible way to search through large amounts of data by creating and editing search conditions.
Any user of the Matrix42 platform, would it be end-users, application administrators or any other person who has access the application can create, run, save and reuse the search filters. At the same time, search filters are not intended to substitute the other provided by default search options of the Matrix42 platform.
Search options can be conventionally classified as:
- simple search has a set of forms that a user fills in, such as global search, keyword search on particular pages or through columns with specific data where the page layout is based on the Dataset View;
- advanced search or the search filters.
The search filters are another search option, which additionally provides numerous opportunities for:
All users:
- configuring advanced search criteria;
- creating simple queries with provided in the application hints;
- immediately retrieving results;
- saving and reusing search filters;
- providing quick access to the filters right from the application's toolbar or Filter Panel;
Application Administrators:
- creating, managing and sharing search filter settings to other users;
- mastering data queries by creating complex conditions defined as ASQL expressions in the search filters.
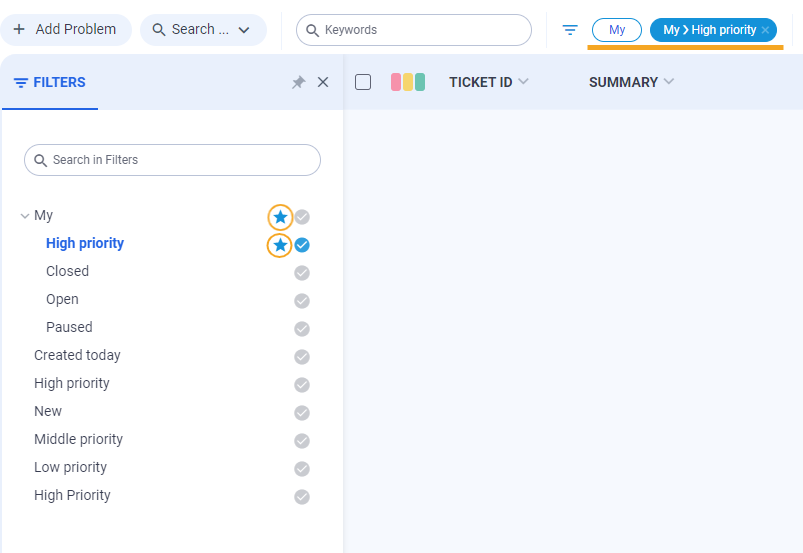
In the New Look, a new approach to adding search filters was introduced. The Filter Panel is now the default for each page where filters are predefined. Previously predefined filters are moved to the toolbar as pills.
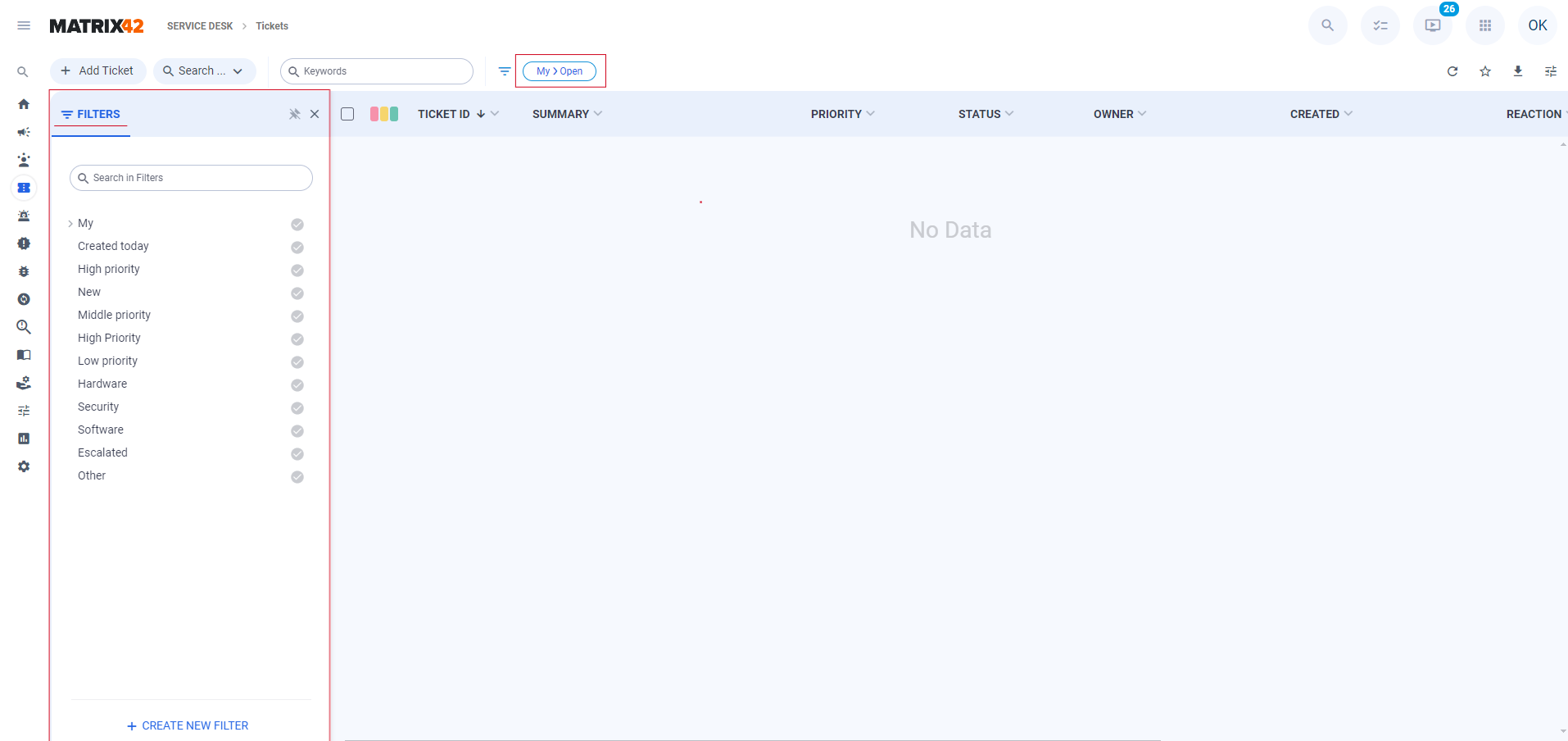
Filter Panel options
If no filters were previously defined on the current page, the filter panel will not be displayed, but it can be accessed by clicking the Show Filters button in the Toolbar.
After opening of Filter Panel users can personalize it according their taste:
- Pinned Filter Panel (Default behavior) - Auto opens the Filter Panel on each page with predefined filters.

- Unpin Filter Panel - Deactivate auto open for users in all dataset views.

- Close Filter Panel - Hides panel without personalization.

Choose/withdraw filter in a Filter Panel
While navigating through the Filter Panel, users can select a filter by clicking on the desired option from the list of available filters. The filter will be instantly applied and displayed on the toolbar, and the data will be promptly filtered according to the conditions specified in the filter. Certainly, users can select not just one filter but multiple filters simultaneously, and all criteria specified in the filter conditions will be adhered to when displaying the data.
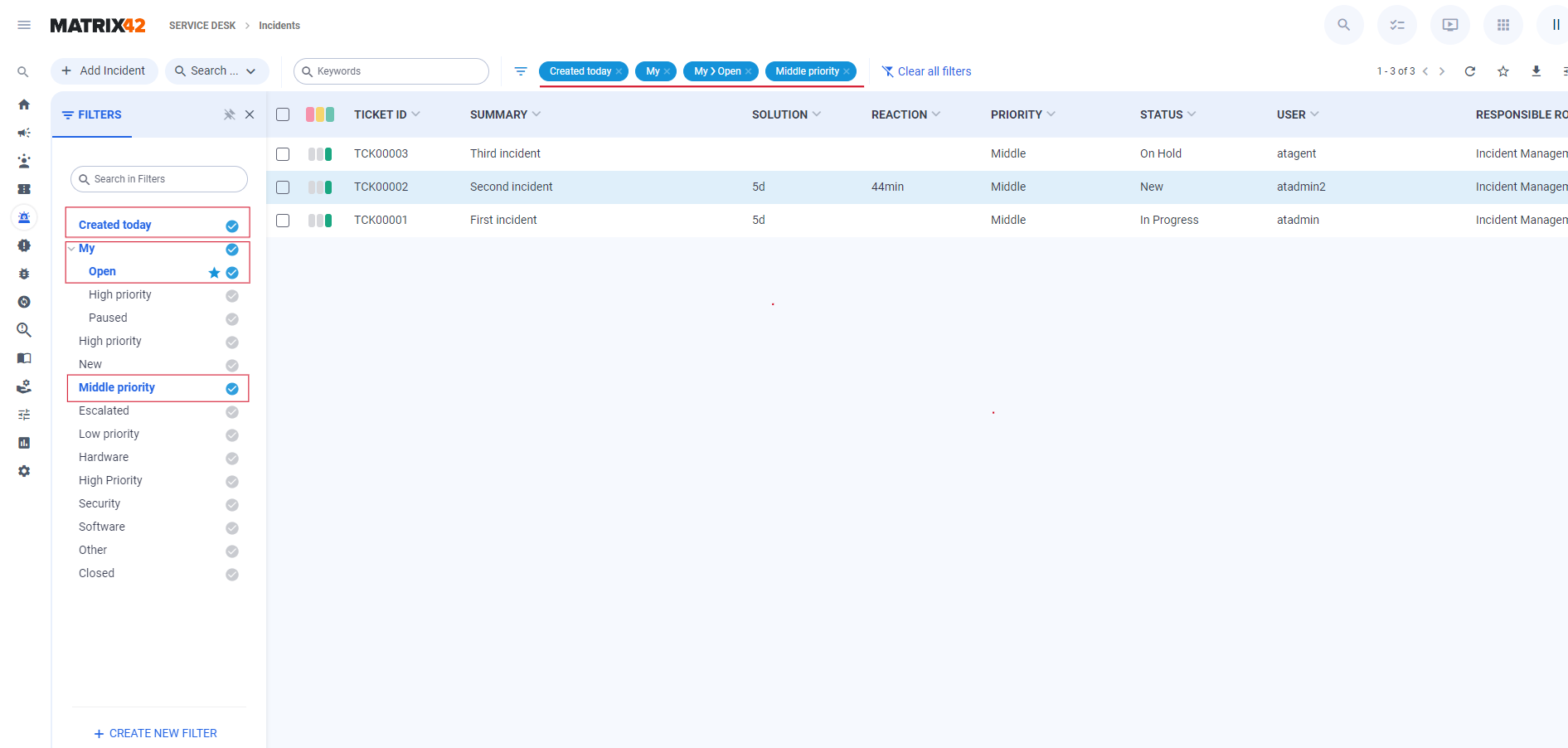
If a user selects a large number of filters and there is not enough space on the toolbar to display them all, a More button appears. This button indicates the number of filters that didn't fit on the toolbar, and additional information about them can be viewed in a tooltip when hovering over the button.
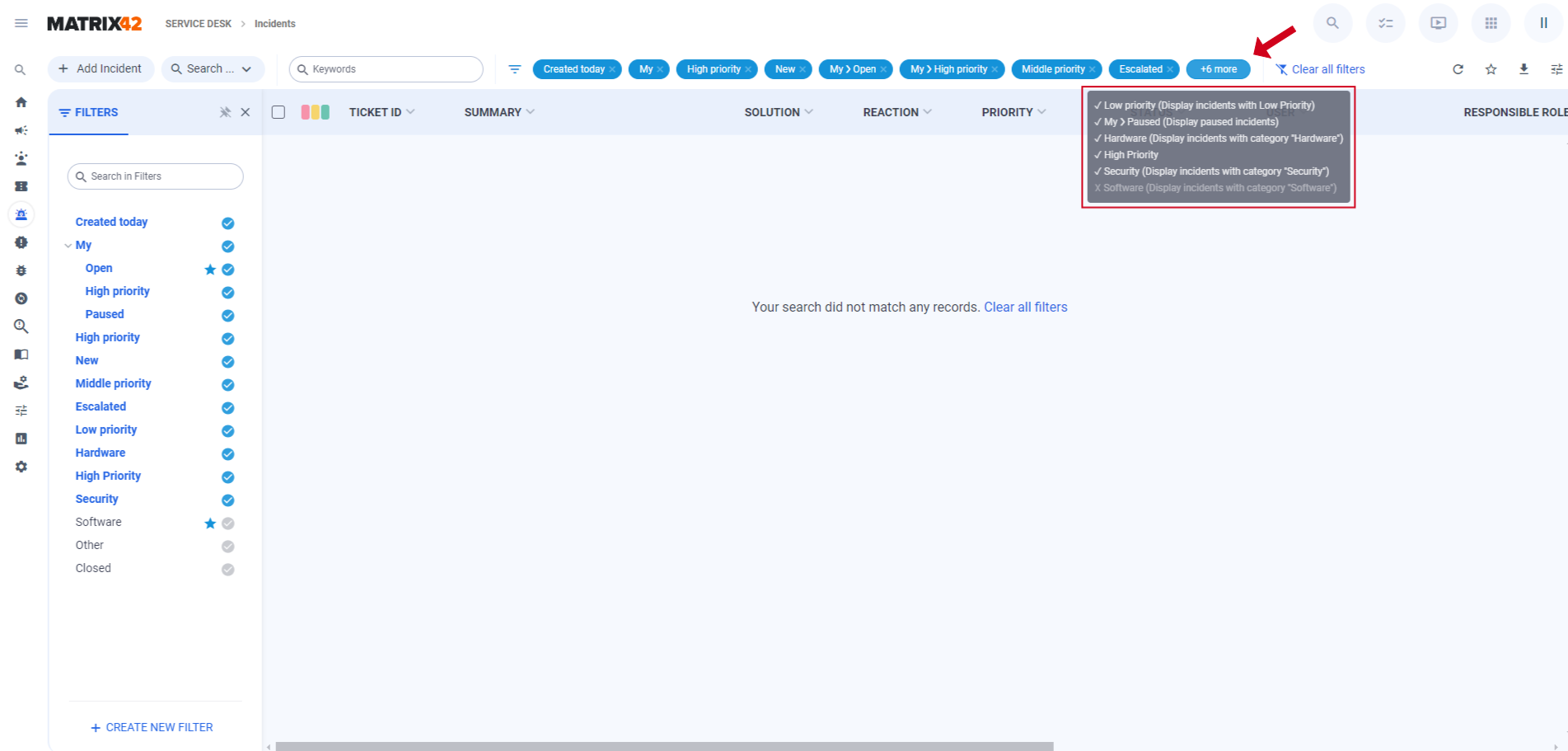
To remove a selected filter, users can click on the pills in the toolbar or press on the selected filter in the Filter Panel. To reset all selected filters at once, users can click on the Clear All Filters buttons.
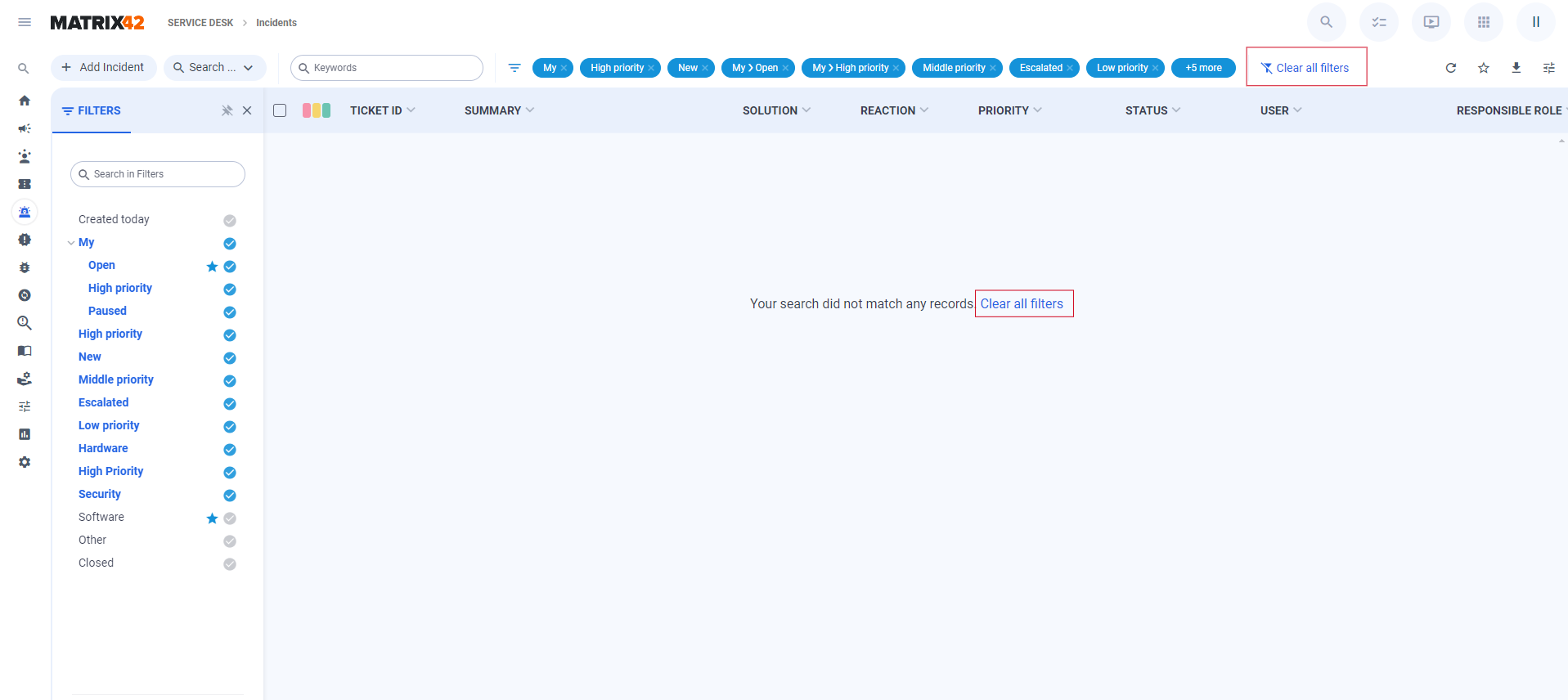
Creating a new Search Filter
You can create and reuse Search Filters from:
- the User Interface of any application via Filter Panel (Advanced Search now is a part of a Filter Panel);
- Administration application from the:
- User interface menu → Search Filters page;
- User interface menu → Layouts → Dataset Views settings → Filters tab.
User interface
To create a Search Filter for a specific page from the User Interface:
Filter Panel → click the Create New Filter button → click the Add Conditions button → choose the needed conditions and set their values → click the Test Query button if you want to precheck the filtered result → click the Done button to save and apply the newly created filter immediately.
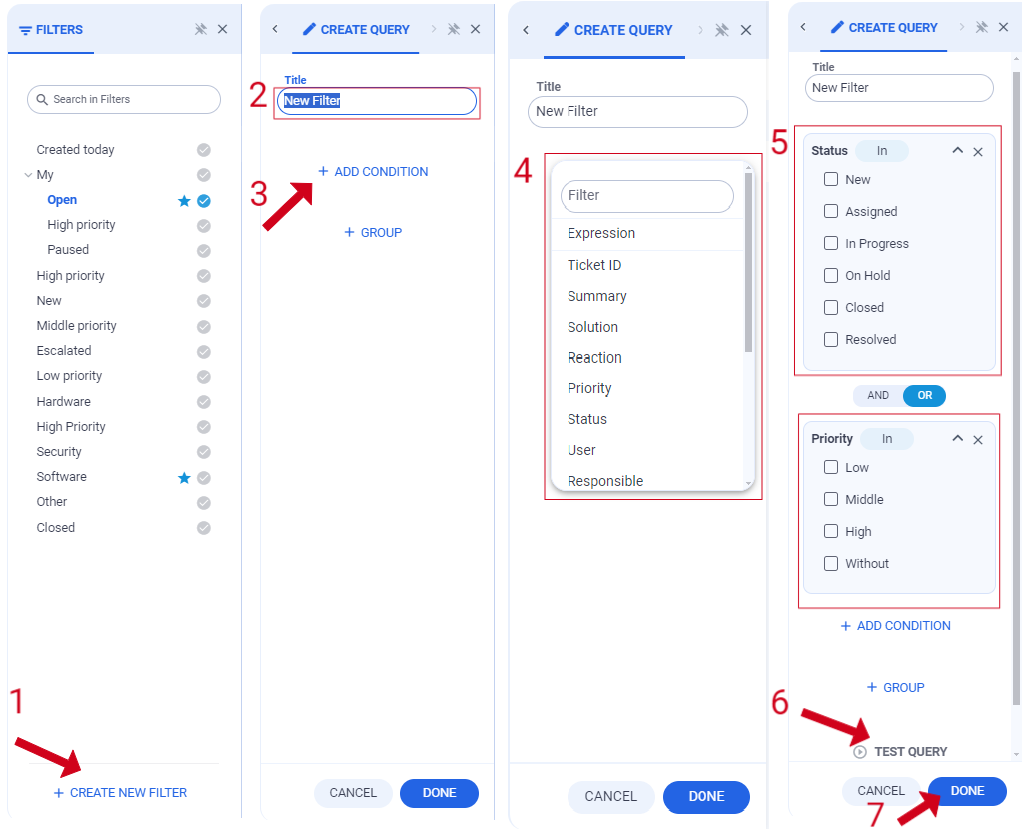
Created search filters are not available for all users of the application by default. End-user: creates and applies search filter settings locally. No other user has access to them, except for the application Administrator. Administrator: creates search filters locally, for displaying only in his/her user account. Additionally, the Administrator can share access to any filters created by any user of the system globally, for the entire application, user roles, user groups, etc. When a filter owner deletes the search filter it is deleted for everyone who had shared access to this filter.
Administration
To create a Search Filter from the Search Filters grid go to Administration application→ User Interface → Search Filters → Add Data Query Filter and fill out the following fields:
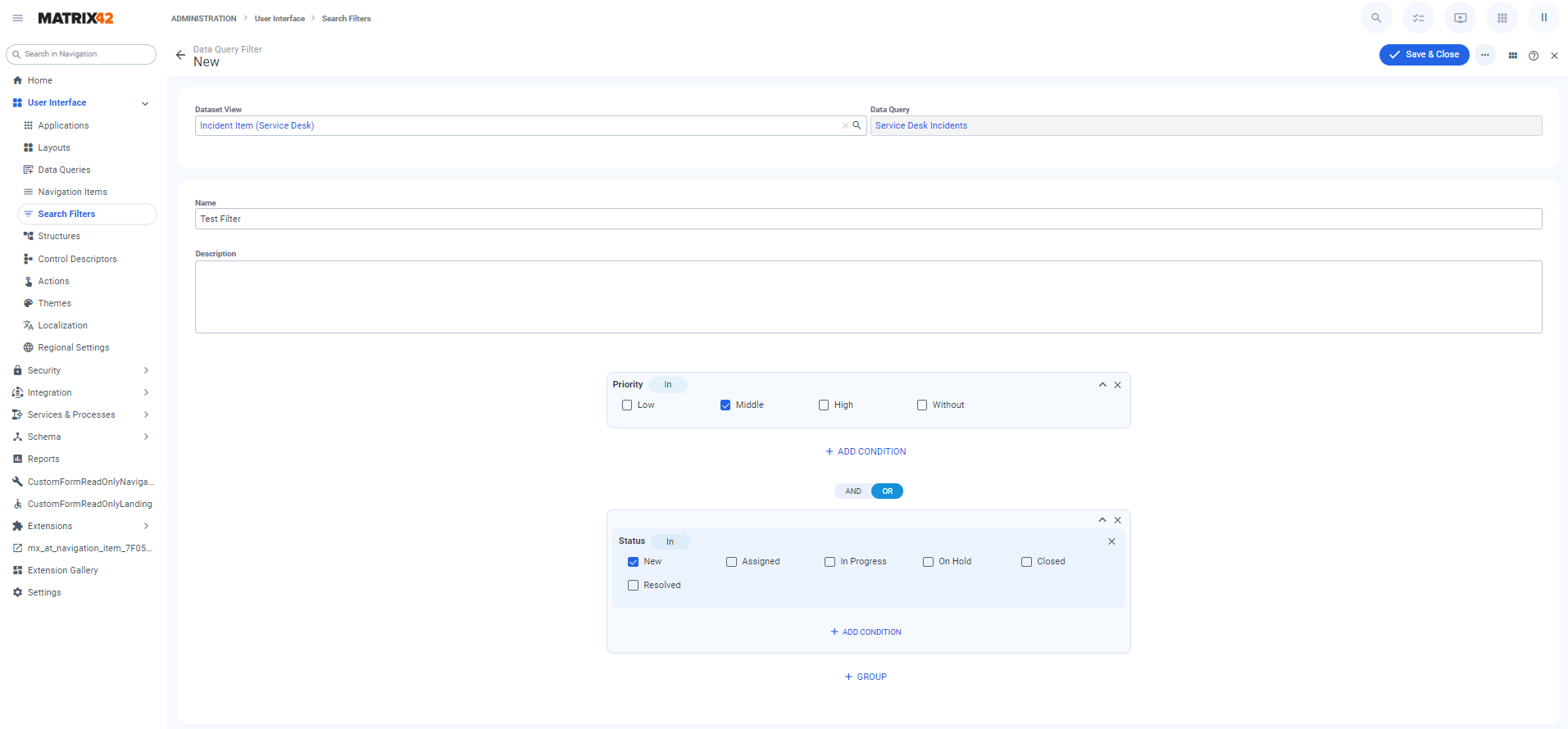
Dataset View: Choose a page layout of Dataset View type for which you would like to create a Search Filter. Start typing the name of the Dataset View for suggestions of the layout and application where it is used. The User Interface does not require this field as the Dataset View is automatically detected by the system based on the page you have opened.
Data Query: Data Query is automatically detected and assigned based on the selected Dataset View. Data Query pre-defines a set of fields that can be queried by the search filter.
Save & Close: to save the changes and close the page.
The set of fields and settings is mostly the same as in the User Interface.
Specifying Search Query conditions
Basic terms and principles
Search filters are based on queries or questions with one or multiple conditions expressed in a formal way. Search filters allow users to create complex questions and as a result, retrieve more specific information that meets their goals and facilitates their day-to-day work in the Matrix42 applications.
A query has the following parts:
-
Field: a specific type of information which serves as a source of the data that will be searched through. In a technical sense, this information is an attribute or the column name of a database table, for example, user id, incident summary, service description etc. Displayed in the drop-down list fields are pre-defined by the corresponding to the current layout Data Query. Only columns with the Search Display Type option set to "Yes" are available.
-
Value: the actual data or an equivalent of the search keyword you are looking for in the filtered data. Value may also be pre-defined according to the selected field type (e.g. true/false) or may require manual data input;
-
Operator: a reserved word that is used to perform the comparison, arithmetical or logical operations and relate the selected field to a specified value. Common operators include equals, not equals, is set, contains, less than, etc. and are auto-suggested.
-
Condition: query builder provides AND condition and OR condition which can be combined in Group and used to filter records based on more than one condition. When combining conditions Group acts just as parentheses in maths so that the database knows in what order to evaluate each condition.
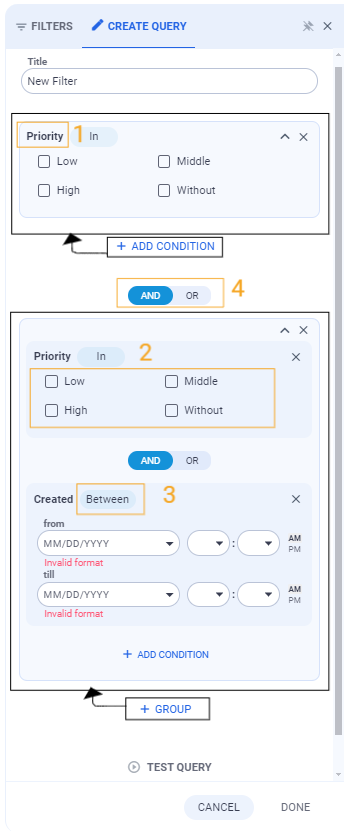
Editing search filter query conditions in the User Interface
Add as many conditions to the new Search Filter as you need and click Save.
You can add and set up as many Search Filters for the same Dataset View as you need.
Operators in Search Filters
Advanced options: Expressions
Advanced Users have the option to create a Search Filter based on the Expression condition, where they can provide any ASQL based query.
This option allows creating complex queries and is available for Administrators only.
So the Expression field takes an ASQL query as its value as follows:
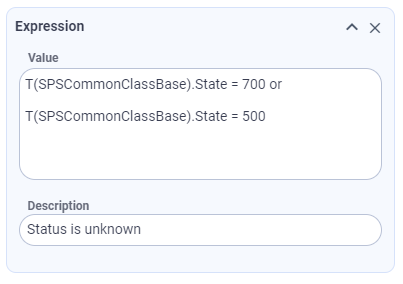
Description of an entered query is required as the value, in this case, may nor be self-descriptive as in the other set of fields provided for a Dataset Query.
Attribute-based operators
When a user selects one of the suggested fields, the available operators are automatically provided based on the type of the selected data attribute:
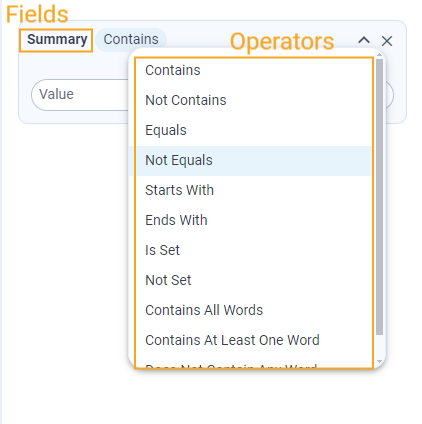
So depending on the field the user selects in condition picker, different operators are available:
| Field/Attribute type | Available operators |
| Date time |
|
| Pickup |
|
| Text |
|
| Relation | |
| Boolean |
|
Filter Options
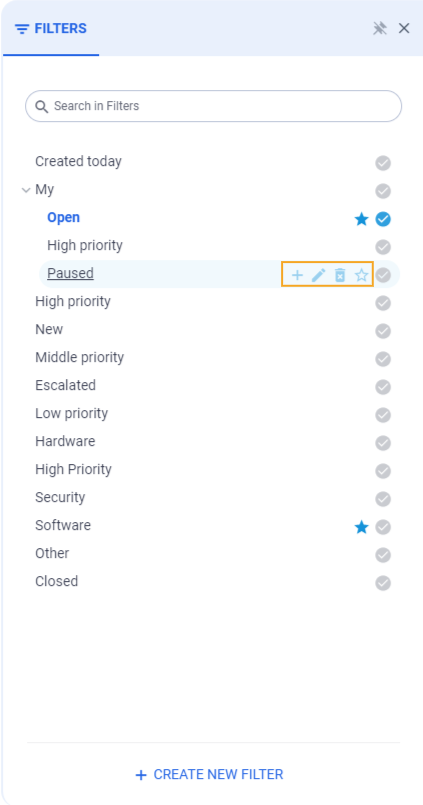
In Filter Panel now available for each filter a few options:
Create New Filter
In the New Look, filters with a parent relation are hierarchical, and their parent filter is automatically applied when set. Pills in the interface provide information indicating that the applied filter also affects the parent, enhancing the user's understanding of the filter hierarchy.
In order to create a hierarchical filter: Select a filter to serve as the parent, then add a title and define conditions for the child filter. Click Done to confirm. The newly created child filter will be applied instantly to the content, filtering it based on the specified conditions.
Please note that the hint message will not reappear if the user closes it once.
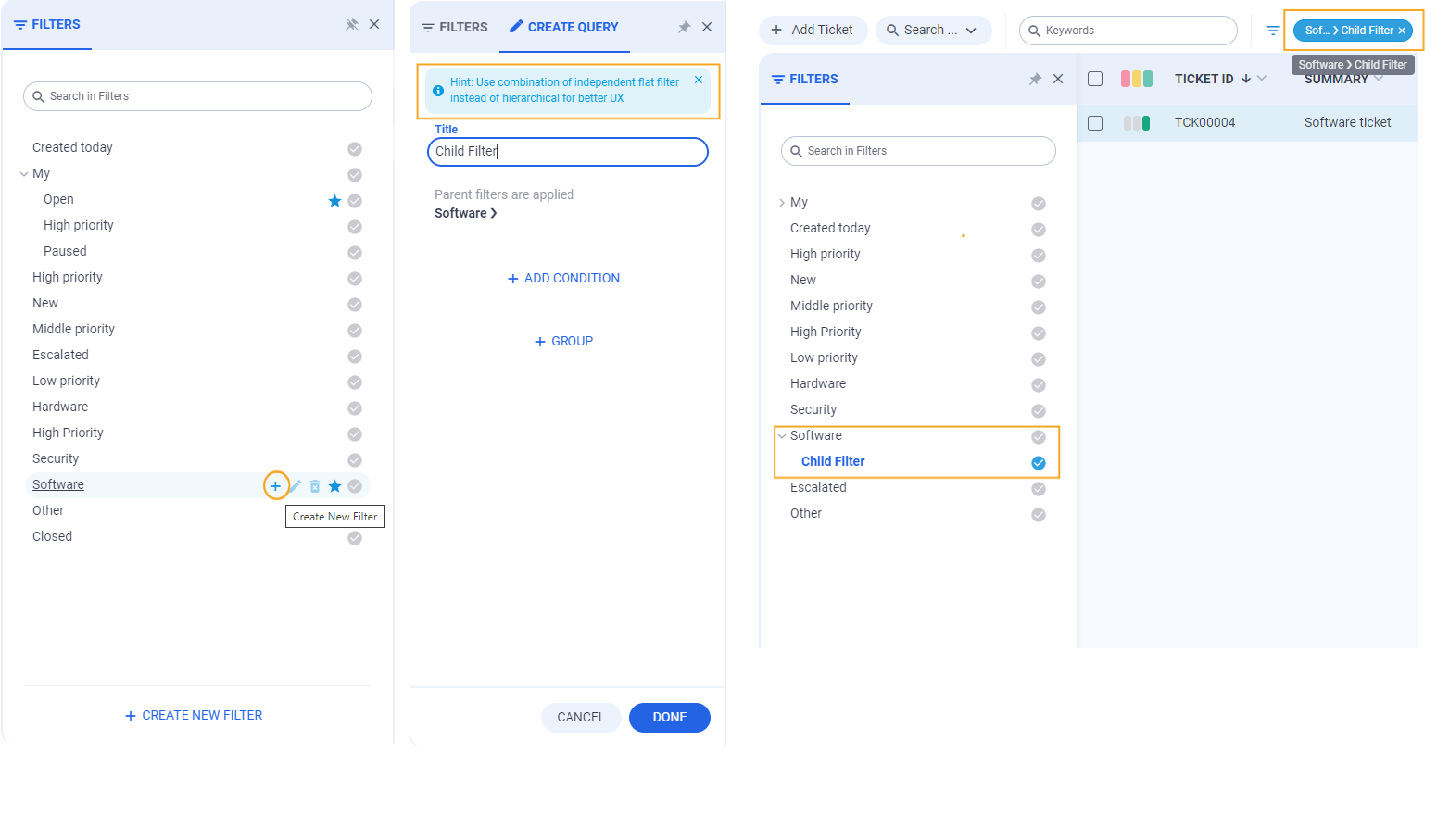
Edit this Filter
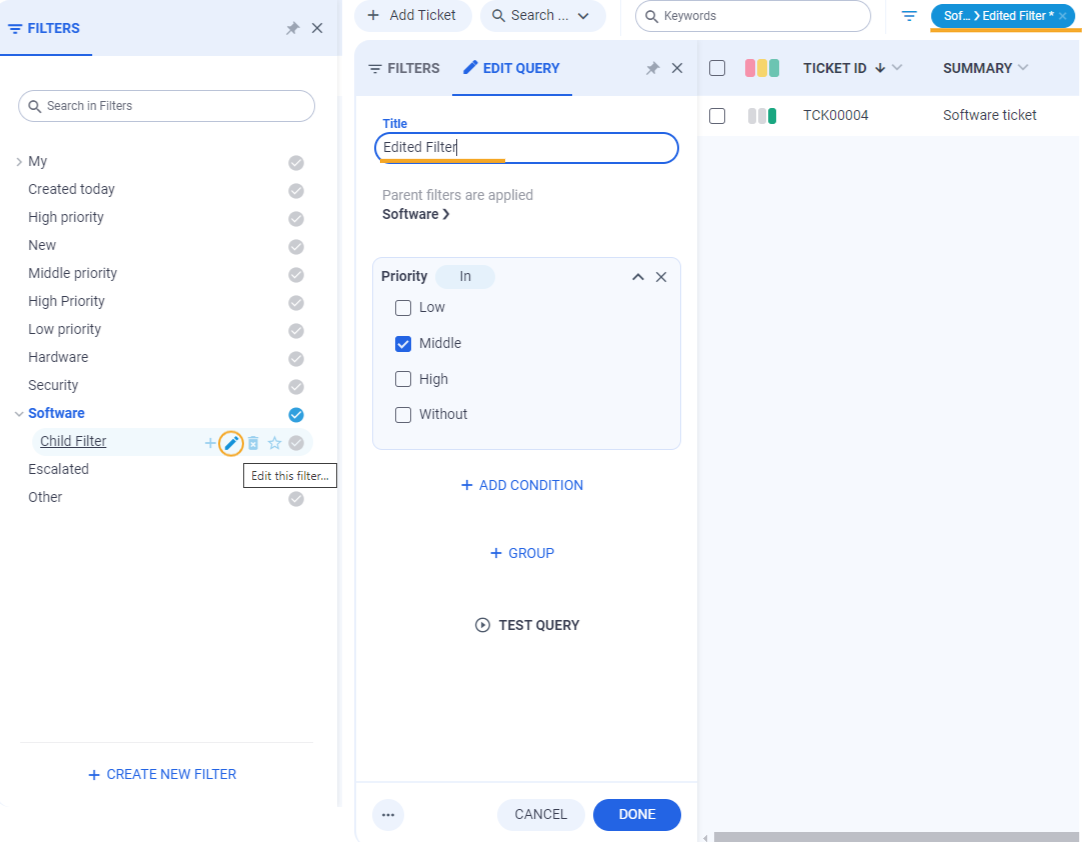
Editing filters in the Filter Panel is straightforward; both active and unselected filters can be edited. To edit a filter: Select the filter that needs to be edited, then click the Edit this filter button. Modify the necessary conditions or titles (note that in the toolbar, this filter will be marked with a asterisk until editing is complete), and click the Done button. The changes will be applied immediately to the current page.
Delete this filter
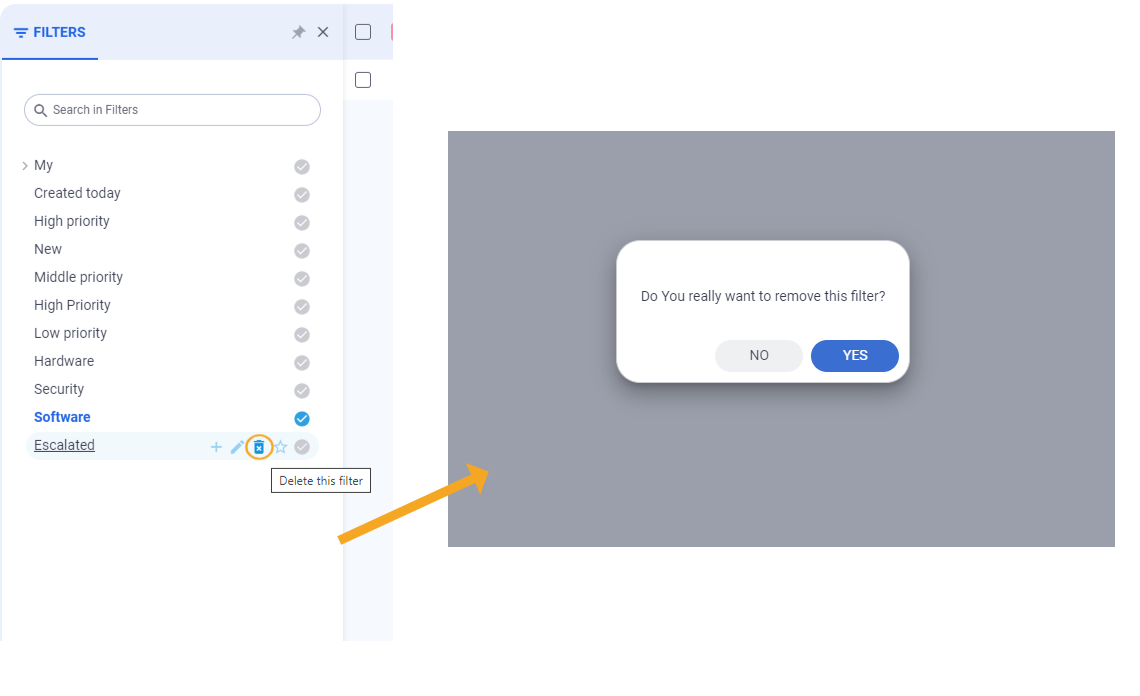
Deleting filters in the Filter Panel is straightforward; both active and unselected filters can be removed. To delete a filter: Select the filter that needs to be deleted, a confirmation form will appear, click the Yes button, and the filter will be immediately removed.The filter will be immediately removed from the Filter Panel.
Show in toolbar
Show in toolbar button allows user to add filters to their favorites list in toolbar for quick access and future use; both active and unselected filters can be added as favorites to toolbar. The Filter Panel shows all filters based on priorities and configurations set for display in the Filter Panel. Default filters are initially marked as favorites, but users have the option to unmark them. Additionally, if a filter is applied but not marked as a favorite, it will still appear in the panel for user reference. To add filters as favorites and display them in the toolbar every time a page is opened on which they were added: Select the filter that needs to be shown in toolbar and click Show in toolbar button, filter will be immediately applied to the toolbar.